Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)
Shockwave therapy was first invented by EMS (electromedical systems), a brilliant German biomedical research and development company more than 40 years ago. Their shockwave technology invention has permanent, world-wide patent protection so no other companies can ever copy their ingenious design. Today they remain the world’s leader in shockwave therapy technology still producing the most powerful, most effective shockwave therapy technology in the world.
The contents of this document, illustrating the effectiveness, wide-range of chronic pain conditions we have successfully resolves, and speed in doing so, are all based upon EMS Swiss Dolorclast Power + Shockwave Therapy Technology.
(Tap or click to scroll to section)
Section 1: Introduction to Shockwave Therapy
Section 2: Types of Shockwaves: Radial vs Focused
Section 3: How Acoustic Shockwaves are produced & work
Section 4: Conditions Resolved with Shockwave Therapy
Section 5: Why Shockwaves don’t harm healthy tissue
Section 1: Introduction to Shockwave Therapy (ESWT)
Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy, or shockwave therapy as it is known, is the therapeutic use of extremely powerful, deep reaching acoustic (sound) waves, to effectively break apart painful soft tissue dysfunctions and calcifications in the tissues and joints of the body.
This is the same revolutionary technology used in hospitals around the world to break apart kidney stones.
Shockwaves are not at all electrical as their name may imply. They are also not to be confused with other technologies such as Ultrasound, TENS, IFC, or muscle stimulators. The term “Shock” wave got its name in physics due to the high speed and extremely powerful nature of their acoustic waves.
This advanced therapy generates powerful acoustic waves to create gas molecule expansion pressure in tissues, strong enough to disrupt a variety of painful dysfunctions and calcifications, that arise in those who suffer with chronic pain, while leaving healthy tissue unharmed.
Shockwaves are used therapeutically to break apart extremely painful calcium deposits from finger and toe joints (bunions, arthritic spurs), calcium deposits in damaged tendons (calcific tendonitis), calcium deposits in damaged muscles, and to completely dismantle the fibrotic twisted/tangled fibres in myofascial adhesions which develop in muscles/tendons/ligaments, responsible for so many chronic pain conditions. These myofascial adhesions along with tendinopathies, heel spurs, pinched nerves, general muscle fiber damage, ligament sprains, chronic inflammation, and pinched nerves are all examples of how widespread pain can manifest itself in knees, hips, low back, neck, arms, and legs. EMS Shockwave therapy is the only technology able to break apart the core dysfunctions responsible for all these conditions.
For nearly 20 years, we have refined and enhanced the use of this world-leading technology from EMS in our mission to eliminate chronic pain.
The proprietary treatment protocols we developed over the past 20 years have leveraged EMS technology to help us resolve the many serious chronic pain conditions we are now known for resolving.
We were among the first therapy clinics in Canada to adopt this groundbreaking technology nearly two decades ago, and have administered almost 300 million acoustic waves to date, resolving various chronic pain conditions to sufferers around the world. We are the busiest users of the technology in Canada.
When paired with our founder’s unique ability to identify causes for chronic pain by touch, EMS shockwave technology has played a critical role in resolving even the most stubborn chronic pain conditions.
Section 2: Types of Shockwaves: Radial vs. Focused
Radial Shockwaves
disperse in a radial (round) pattern, increasing in the diameter and depth as they travel deeper into the soft tissues of the body. They are preferred to resolve larger regions of dysfunction in muscles, tendons or ligaments.
The success of any shockwave therapy treatment directly depends on the knowledge and skill of the therapist, as well as with the quality of shockwave unit being used.

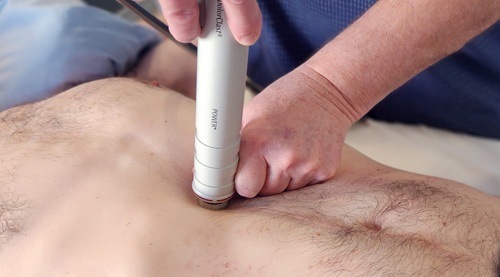
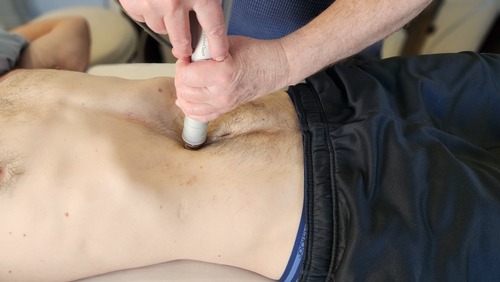
Radial Shockwave Therapy administered at the clinic to treat Abdominal Adhesions, Burning Mouth Syndrome and Bunions.
Focused Shockwaves
Do not disperse, but rather remain in a narrow beam pattern. Focused shockwaves are ideal for small, extremely dense dysfunctions such as chronic tendonitis and heel spurs. These shockwaves require extreme skill from the therapist as an incorrect application angle of the shockwave beam could miss the targeted tissues, resulting in a totally ineffective treatment. Both have their advantages and disadvantages in treating conditions, to be chosen by the therapist based on the condition being treated.

Section 3: How Acoustic Shockwaves are produced & work
This explanation may be confusing at first, so you are encouraged to read it several times to fully understand what shockwaves actually are.
Producing a Shockwave:
An acoustic wave applicator which resembles a gun is depressed against the skin over a region to be treated.
Inside this applicator, a metal bullet is propelled down a long cylinder driven by compressed air at 90-120 PSI to strike a metal adapter at its tip thus producing very unique and powerful acoustic waves.
These acoustic waves enter the body through a gel applied to the skin to allow propagation of the waves.
Each acoustic wave has a leading-edge called a “wavefront,” where its energy (ability to do work) is located. This potential energy comes from both the air pressure from a compressor used to propel the bullet with extreme force to strike the metal applicator tip, and from the speed this bullet travels through the cylinder in the applicator.
This high energy wave front resembles a large rock thrown with high speed into water, and the resulting water disruption waves it creates is the wave front.
The ability for acoustic waves to enter the body, and accomplish therapeutic work, directly come from this high energy wavefront. The more energy an acoustic wave possesses, the deeper it can reach into the body, and more capable it’s wavefronts will be in penetrating deep lying and hardened dysfunctions to achieve treatment results.
Here’s how a shockwave is produced:
- Acoustic waves begin entering the body when the gun-like applicator is depressed against the skin, moistened by a special anti-bacterial gel allowing for its impulse penetration.
- The high-speed acoustic pressure waves cause gas molecule expansion within the blood and lymphatic fluids bathing muscles/tendons/ligaments, to rapidly expand to many times their size.
- These rapidly expanding gas molecules cause a sudden stretch pressure on the twisted/tangled/glued fibres within the problematic adhesions, creating cavities or hollow voids in muscles, tendons, and ligaments, in a process termed “cavitation.”
- Voids are like a vacuum and have no pressure within them, so rapidly collapse on themselves (implode) far more rapidly then when they stretched , thus generating a high speed implosion wave (shockwave) of force on the tissue. Think of the process as slowly stretching out an elastic (creating the void), then releasing it (implosion). This enormously high-speed expansion/implosion wave is the starting point to the creation of a shockwave.
- Billions of these high speed expanding/imploding cavitational voids create a rapidly moving wave through the tissues which is finally the creation of a shockwave.
- These shockwaves are sufficiently disruptive to cause myofascial adhesions and small calcium deposits to break apart.
The key to understand this process is that the expansion and implosion of gas molecule cavitation takes place many times per second. Its like stretching out an elastic and letting it snap back. This constant stretch/contract action takes place hundreds and thousands of time during a treatment.
Shockwave devices can be thought of as the acoustic wave generators which cause the cavitational process to occur, not as a device which specifically delivers shockwaves into the body. Shockwaves are made in the body with the help of this acoustic wave cavitational action.
Note
Healthy muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves are not affected by shockwaves as they can easily absorb the cavitational and thus shockwave forces. The acoustic waves simply bounce off bones and hyaline cartilage having no affect positive or negative on them.
Section 4: Conditions resolved with Shockwave Therapy
The following information is based upon the conditions we have developed highly successful protocols to treat using EMS technology over the past 20 years. We realized many years ago that we needed the power and capability afforded by this technology to achieve success treating these conditions.
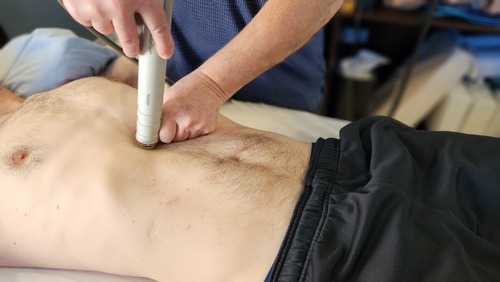
Disintegrate collagen bonds in myofascial adhesions responsible for:
Shockwave Therapy administered at the clinic to disintegrate collagen bonds in myofascial adhesions – Abdominal Adhesions.
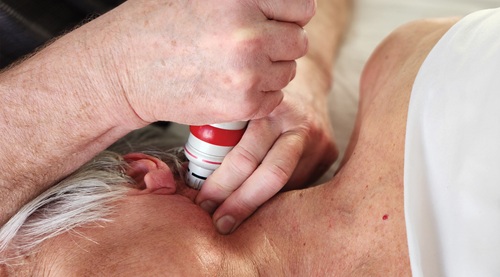
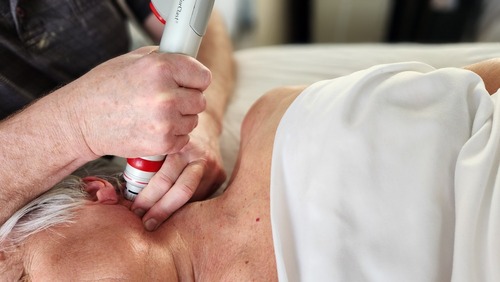
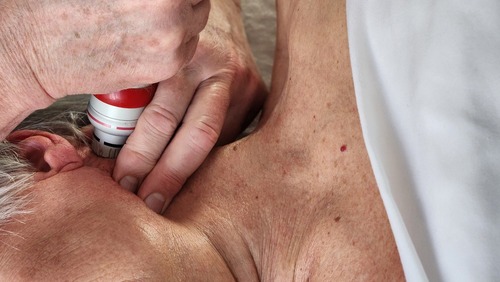
Peripheral Nerve Compressions:
- Sciatica
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Pelvic Pain syndrome/Pudendal Neuralgia
- Burning Mouth Syndrome – Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Belles Palsy
- Femoral Impingement
- Morton’s Neuroma
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Exiting Spinal Nerve Compression (Arthritis)
- Vagus Nerve Compression
- Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome (Foot)
Shockwave Therapy administered at the clinic to treat peripheral nerve compressions – Burning Mouth Syndrome.
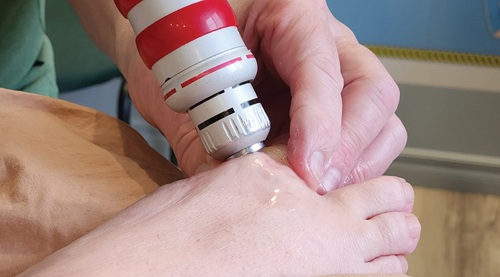
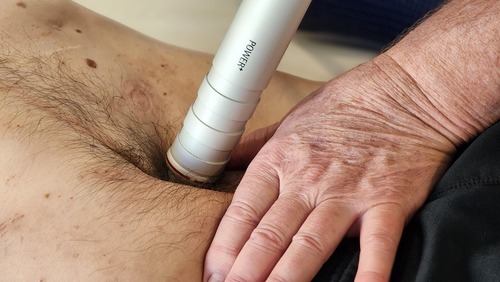
Removing Calcifications:
- Bunions
- Hammer Toes
- Finger/Toe Arthritic Calcifications
- Haglund’s Deformity (Achilles/Heel junction)
- Heel Spurs
- Chronic Muscle Fiber Calcifications
- Calcific Tendinopathy
- Thumb Arthritis
Shockwave Therapy administred at the clinic to break appart calcifications – Bunions.
Section 5: Why Shockwave Therapy does not harm healthy tissue
The acoustic waves of a shockwave applicator cause the gas molecules (oxygen/carbon dioxide/nitrogen…) in blood and lymphatic fluid to expand to many times their normal size. This expansion of gases creates increased internal pressure in the tissues being treated, disintegrating the notorious, cross-bridged collagen bonds common to myofascial adhesions, some forms of scar tissue, and unwanted calcifications.
There is a unique and remarkable relationship between the concentration of gas molecules in the blood and lymphatic fluid in the soft tissues of the body, and the degree of elasticity these tissues possess. The higher concentration of gases, the higher elasticity the tissue has. The lower the concentration of gases, the lower elasticity the tissue has.
Muscles
Muscles and their fascial tissue component possess the highest degree of elasticity of all the body’s soft tissues. They equally possess the highest concentration of blood and lymphatic fluid, because of their high demands for oxygen to provide essential energy to stretch and contract.
When acoustic waves reach the billions of microscopic gas molecules in blood and lymphatic fluid, the molecules explode in size, causing an extremely high internal pressure to develop in the muscle’s fibres. This internal pressure is sufficient to stretch the fibres enough to break apart the cross-bridged collagen bonds in the adhesion, but not enough to tear the muscle’s fibres.
There are simply not enough gas molecules per square centimeter in the blood or lymphatic fluids to tear these elastic muscle fibres.
Tendons and Ligaments
Tendons and ligaments have no blood in their fibres, only small amounts of lymphatic fluid. The amount of this lymphatic fluid per square centimeter is far less than in muscles because tendons and ligaments are extremely hardened structures that can expand only 3% of their original size, with a limited amount of lymphatic fluid able to flow through their densely packed fibers.
The good news is that shockwave’s acoustic waves simply cannot cause enough expansion in the small amount of lymphatic fluid present, to stretch the fibres more than 3%. There is simply not enough concentration of gas molecules per square centimeter to do so.
However, the expansion pressure is sufficient to break apart the collagen bonds in adhesions and unwanted calcifications that may develop.
Internal Organs
The internal organs in the body have varying degrees of elasticity based on their diverse composition of elastic muscle and less elastic structural connective tissue (tendon/ligament) matrix.
An essential aspect for all organs to function correctly is to be able to stretch as they fasciculate in a unique rhythm set by the blood flow through their tissue fibres.
As the shockwave’s acoustic waves reach organ tissue, the amount of tissue stretch caused by the expanding gas molecules is directly proportional to the concentration of each tissue type comprising that organ.
Tissue comprised of 100% muscle tissue like blood vessels, stomach, and heart for example, will stretch, while tissue comprised of 50% muscle, and 50% denser connective tissue fibres such as the colon will stretch less.
When acoustic waves of shockwave therapy reach any organ, they will cause each tissue type to safely expand within their specific limits as mentioned above, sufficient to disintegrate myofascial adhesions but not enough to tear organ tissue fibers.
Abdominal Adhesions
Finally, we get to those infamous myofascial adhesions that can ruin a person’s life.
Every organ in the abdomen has the same physiology with respect to varying degrees of tissue types, elasticity, and blood and lymphatic fluid concentrations, as described above.
Shockwave therapy into the abdomen targets myofascial adhesions in the abdominal muscles and their inner lining tissue, connective tissues holding all organs in their correct position, omentum, ligaments, and the organ’s outer connective tissue matrix adhering it to adjacent organs.
The shockwave’s acoustic waves physiologically cannot harm any organs or tissues in the abdomen due to the ratio of gas molecule concentration versus tissue elasticity.
This ratio of gas molecule expansion versus tissue elasticity is the genius research conducted by EMS Technologies, the German company who invented shockwave therapy over 40 years ago, and is the version of the technology we exclusively use in our clinic in Canada every day to break apart myofascial adhesions, scar tissue, and calcifications wherever they reside.
Note
EMS Shockwave therapy is used daily to break apart kidney stones for a good reason. Their acoustic waves are easily absorbed by the high/medium/low elastic tissues comprising the kidney and see their gas molecules expand in the ratio of concentration versus the elasticity factor but have no adverse effect on healthy tissues in the kidney.
However, the acoustic waves do possess enough energy to vibrate the stone to fracture it into smaller pieces.
Shockwave therapy physiologically cannot harm healthy tissue, no matter where in the body their acoustic waves are applied.